In our modern society, we rarely consider books to be dangerous items. However, certain books contain elements so hazardous that they require scrutiny before being placed on the shelves of public libraries, bookstores or even private homes.
The Poisonous Book Project, a collaborative research project between Winterthur Museum, Garden & Library and the University of Delaware, is dedicated to cataloguing such books. Their concern is not with the content written on the pages, but with the physical components of the books themselves — specifically, the colours of the covers.
The project recently influenced the decision to remove two books from the French national library. The reason? Their vibrant green cloth covers raised suspicions of containing arsenic.
This concern is rooted in historical practices in bookbinding. During the 19th century, as books began to be mass produced, bookbinders transitioned from using expensive leather covers to more affordable cloth items. To attract readers, these cloth covers were often dyed in bright, eye-catching colours.
Green, yellow, red
One popular pigment was Scheele’s green, named after Carl Wilhelm Scheele, a German-Swedish chemist who in 1775 discovered that a vivid green pigment could be produced from copper and arsenic. This dye was not only cheap to make, it was also more vibrant than the copper carbonate greens that had been used for over a century.
Scheele green eventually fell out of favour because it had a tendency to fade to black when it reacted with sulphur-based pollutants released from coal. But new dyes based on Scheele’s discovery, such as emerald and Paris green, proved to be much more durable. They were quickly adopted for use in various items, including book covers, clothing, candles and wallpaper.
These pigments, however, had a significant drawback: they degraded easily, releasing poisonous and carcinogenic arsenic. The frequent reports of green candles poisoning children at Christmas parties, factory workers tasked with applying paint to ornaments convulsing and vomiting green water and warnings of poisonous ball dresses raised serious concerns about the safety of these green dyes.
This issue became so notorious that in 1862, the satirical magazine Punch published a cartoon titled The Arsenic Waltz”, which depicted skeletons dancing – a grim commentary on the deadly fashion trend.
The harmful effects of these pigments have even been implicated in Napoleon’s death from stomach cancer. Napoleon was particularly keen on the new green colours, so much so that he ordered his dwelling on St Helena, where he was exiled, be painted in his favourite colour.
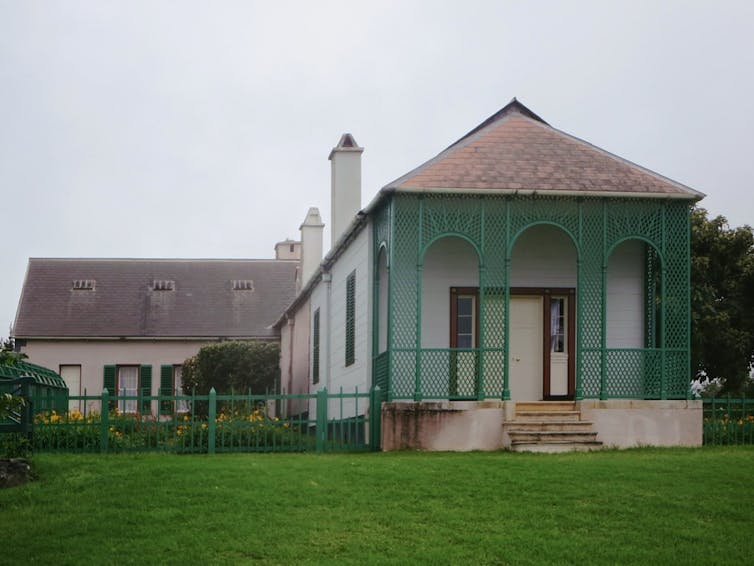

The theory that the arsenic in the walls contributed to his death is supported by the high levels of arsenic detected in samples of his hair. Despite the clear link between the green pigments and health issues, toxic wallpapers continued to be produced until the late 19th century.
Green isn’t the only colour to worry about, however. Red is also of concern. The brilliant red pigment vermilion was formed from the mineral cinnabar, also known as mercury sulfide. This was a popular source of red paint dating back thousands of years. There is even evidence that neolithic artists suffered from mercury poisoning. Vermilion red sometimes appears on the marbled patterns on the inside of book covers.
Yellow has also caught the eye of the poisonous book project. In this case, the culprit is lead chromate. The bright yellow of lead chromate was a favourite with painters, not least Vincent van Gogh, who used it extensively in his most famous series of paintings: Sunflowers. For the Victorian-era bookbinders, lead chromate allowed them to create a range of colours from greens (achieved by mixing chrome yellow with Prussian blue) to yellows, oranges and browns.
Both lead and chromium are toxic. But yellow books are less of a concern than green and red. Lead chromate is not particularly soluble, making it difficult to absorb. It is, in fact, still a widely used pigment.
Practical advice
So what should you do if you come across a green cloth book from the 19th century? First, don’t be overly concerned. You would probably have to eat the entire book before you’d suffer from severe arsenic poisoning. However, casual exposure to copper acetoarsenite, the compound in the green pigment, can irritate the eyes, nose and throat.
It is more of a concern for folks who may regularly handle these books where frequent contact could result in more serious symptoms. Therefore, anyone who suspects they might be handling a Victorian-era book with an emerald green binding is advised to wear gloves and avoid touching their face. Then clean all surfaces afterwards.
To aid with the identification of these potentially hazardous books, the Poisonous Book Project has incorporated crowd-sourced data into their research. The researchers now distribute bookmarks that feature safety warnings and showcase various shades of emerald green to aid their identification. As a result, they have now identified over 238 arsenic editions from across the globe.
![]()
Mark Lorch does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.