A reckless experiment in Earth’s atmosphere caused a desert metropolis to flood.
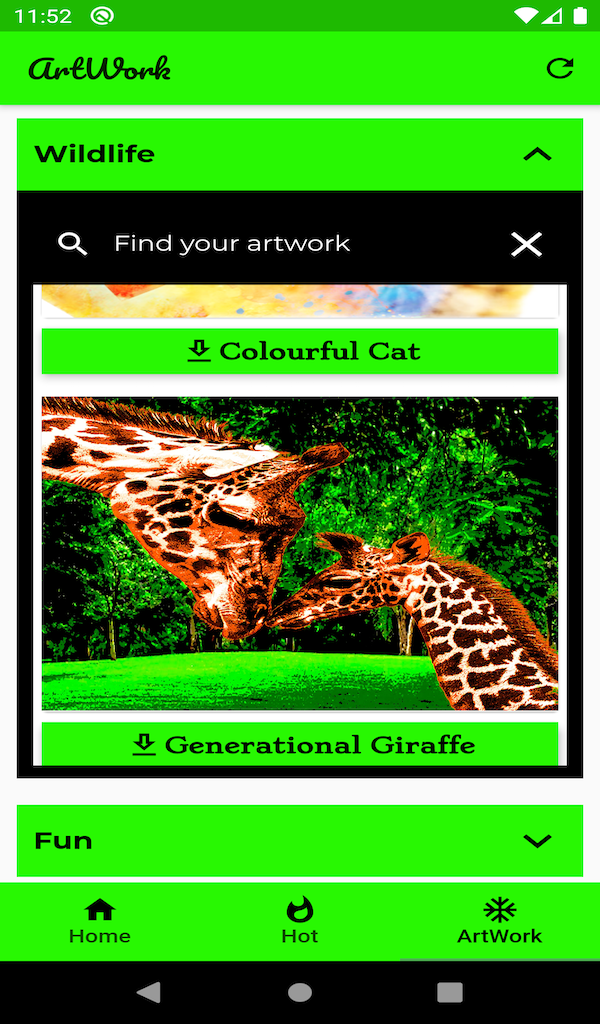
That was the story last week when more than a year’s worth of rain fell in a day on the Arabian Peninsula, one of the world’s driest regions. Desert cities like Dubai in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) suffered floods that submerged motorways and airport runways. Across UAE and Oman, 21 people lost their lives.
The heavy rain of Tuesday April 16 was initially blamed on “cloud seeding”: a method of stimulating precipitation by injecting clouds with tiny particles that moisture can attach to – those droplets then merge and multiply. As the waters receded, however, a more disturbing explanation emerged.
Richard Washington, a professor of climate science at the University of Oxford, has seen the inside of a storm. To confirm if cloud seeding really could breed record-breaking rain, he once boarded an aeroplane bound for a thundercloud over the South Africa-Mozambique border.
“Our mission was to fly through the most active part of the storm, measure it, fly through again while dumping a bin load of dry ice, turn hard and fly through for a final measurement,” he says.
“Apart from the fun of flying through the core of a thunderstorm in a Learjet, I didn’t think much about the time I was lucky enough to be part of that project. Until I heard about the recent freak storm in Dubai.”
What caused the flood?
There are no two identical clouds with which to compare the outcome of seeding, Washington says, so it’s impossible to prove if this technique can change the outcome of a single storm. But by flying a lot of missions, half with cloud seeding and half without, and measuring rainfall between the two, meteorologists eventually showed that cloud seeding did modify rain rates in some storms.
That’s not what caused Dubai’s floods though.

“It turns out the UAE has been running a cloud seeding project, UAE Research Program for Rain Enhancement Science, for several years. Their approach is to fire hygroscopic (water-attracting) salt flares from aircraft into warm cumuliform clouds,” Washington says.
“So could seeding have built a huge storm system the size of France? Let’s be clear, that would be like a breeze stopping an intercity train going at full tilt. And the seeding flights had not happened that day either. The kind of deep, large-scale clouds formed on April 16 are not the target of the experiment.”
For Washington, the more relevant atmospheric experiment is the one each of us is engaged in everyday.
“The interesting thing is that humans have a hard time coming to terms with the fact that 2,400 gigatonnes of carbon (our total emissions since pre-industrial times) might make a difference to the climate, but very readily get behind the idea of a few hygroscopic flares making 18 months worth of rain fall in a day.”
The experiment of our lives
A hotter atmosphere holds more moisture, which can fall as rain. Although last week’s deluge was unusual, the Arabian Peninsula does tend to receive more of its precipitation in heavy bursts than steady showers.
The latest assessment by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) did not predict future rainfall trends for the region but did say global heating is expected to make such violent downpours more frequent and severe.
What is likely to kill more people as temperatures rise in this part of the world is not water, but heat. Tom Matthews (Loughborough University) and Colin Raymond (California Institute of Technology) are scientists who study the shifting climate and its effect on our bodies.
Throughout human evolution, the wet-bulb temperature (how hot it is when you subtract the cooling effect of evaporating moisture, like sweat on your skin) has rarely, if ever, strayed beyond 35°C. At this threshold the air is so hot and humid that you cannot lower your temperature to a safe level by sweating. You overheat and, without urgent medical aid, die.
“The frequency of punishing wet-bulb temperatures has more than doubled worldwide since 1979, and in some of the hottest and most humid places on Earth, like the coastal United Arab Emirates, wet-bulb temperatures have already flickered past 35°C,” Matthews and Raymond say.
“The climate envelope is pushing into territory where our physiology cannot follow.”
Alarmed by how fast we are making the climate unlivable, some scientists have called for emergency measures. Peter Irvine, a lecturer in earth sciences at UCL, proposes dimming the sun by pumping microscopic particles into the upper atmosphere to reflect some of its rays.
Trying to mimic the cooling effect of a volcanic eruption but on a permanent basis (until, presumably, greenhouse gas concentrations can be returned to safe levels) is another gamble with the atmosphere. These layers of gases that surround our planet have nurtured life by keeping temperatures stable and harmful radiation out.
Irvine acknowledges that keeping Earth artificially cool this way is risky, but argues the side effects – like altered wind and rainfall patterns, acid rain and delayed ozone layer recovery – “pale in comparison to the impacts of climate change”.
Catriona McKinnon, a professor of political theory at the University of Reading, has other concerns about attempting to manage solar radiation this way, including the question of who has the right to regulate the global thermostat.
As humanity contemplates another large-scale experiment in our atmosphere, there is another, even bigger one, waiting to be resolved. Its solution is simple: stop burning fossil fuels.
![]()