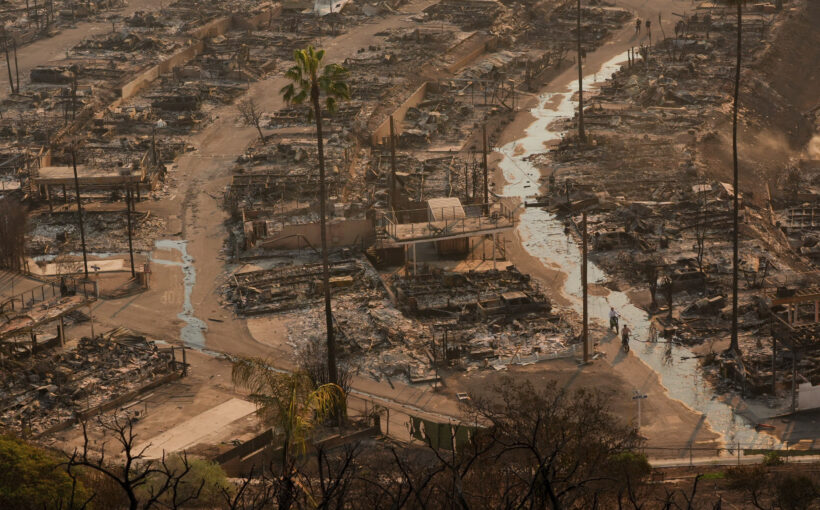
October to April is normally considered to be the wet season in California, yet this January, the region is experiencing some of the most devastating fires it’s ever seen.
As of January 10, five major fires in and around Los Angeles have burned over 29,053 acres, leading to the evacuation of more than 180,000 people, the destruction of over 2,000 buildings (mainly homes), and an estimated damage cost of at least US$52 billion (£42.5 billion). Ten lives have been lost, and these numbers are expected to rise as the fires continue to burn.
The exact causes of each fire are still under investigation. However, several factors have contributed to their rapid spread and intensity.
The seasonal Santa Ana winds are particularly strong this year, bringing low humidity, dry air and high wind speeds. Southern California has received less than 10% of its average rainfall since October 2024, creating dry conditions that make the area highly vulnerable to fire.
Unusually wet winters in both 2022-23 and 2023-24 led to increased vegetation growth, providing more fuel for the fires. This cycle of wet and dry extremes, known as “hydroclimate whiplash”, is part of the increasingly intense climate cycles caused by climate change.
Hydroclimate whiplash can occur virtually anywhere. These cycles can cause extreme wildfires, such as those in California, where rapid vegetation growth is followed by drying. They can also exacerbate flooding when unusually heavy rains hit the dry-baked ground, then run off over the land rather than seeping in, leading to flash flooding.
The human impact of hydroclimate whiplash
Rapid transitions between extreme wet and dry conditions have significant and wide-ranging impacts on people, a focus of my academic research, affecting everything from public health to economic stability and social equity.
As we have seen in California, there is the immediate impact of loss of life, property and livelihoods. We have also seen this during whiplash-induced floods and landslides, such as those experienced across California in 2023 and east Africa in 2024, when years of drought were followed by weeks of rain.
Fires exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular diseases through their polluting smoke. Flooding creates conditions for waterborne illnesses such as cholera, leptospirosis or norovirus to rip through populations. Extreme swings in temperature can also create more heat-related illnesses, as human bodies struggle to adapt quickly. It is estimated that the health-related impacts of climate change will cost US$1.1 trillion by 2050.
But this number pails into insignificance against the projected US$12.5 trillion in economic losses worldwide due to climate change by 2050. Critical infrastructure, including water supply systems, wastewater treatment plants and transportation networks, is at risk of damage or destruction. Food insecurity and scarcity will also increase during hydroclimate whiplash events.
And these impacts are not evenly distributed. While this month’s wildfires are affecting some of the richest communities in the US, it is generally low-income communities and vulnerable populations that are disproportionately affected, with limited resources to prepare for or recover from extreme events. Across the world, poorer populations are experiencing a 24%-48% increase in drought-to-downpour events, exacerbating their vulnerability and widening the health equity gap.
All these events and concerns also lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), resulting from displacement and trauma. Such human impacts are harder to measure, and often under-reported.
Adaptation and resilience
As climate change intensifies hydroclimate whiplash events, the human impacts are expected to grow more severe. Addressing these challenges will require coordinated efforts across multiple sectors, with a focus on both mitigation and adaptation strategies to protect human health, economic stability and social equity.
Governments and local authorities will need to implement co-management approaches for both drought and flood risks, alongside developing more flexible water management systems and infrastructure. Investing in natural infrastructure to enhance biodiversity and ecosystems will reduce risks to humans, both by restricting the effects of climate change and lowering the risks of fire and flooding.
As individuals we can often feel powerless, but environmental campaigns and movements have been highly successful in changing government policies. In the UK, the 2008 Climate Change Act and the net zero by 2050 legislation were the direct result of citizen lobbying and action, and the same can be said for numerous renewable energy transition policies around the world.
In California, we have seen the devastating effect of hydroclimate whiplash – and this won’t be the last we see. By calling on our governments to produce adaptation and resilience strategies that recognise climate change as a long-term human and economic risk factor, we can be more prepared for these events.
![]()
Doug Specht does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.